-
다익스트라 알고리즘 ( Dijkstra Algorithm )자료구조 & 알고리즘 2023. 1. 14. 15:10
Reference : https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dijkstras-shortest-path-algorithm-greedy-algo-7/
다익스트라 알고리즘은 그래프를 이용한 그리디 알고리즘 중 하나이다.
다익스트라 알고리즘은, 주어진 그래프에서 한 점에서 모든 정점까지의 최단경로를 찾는다.
- 시간복잡도 ( Time Complexity ) : O( V^2 ) ( V : 정점 개수 )
- 공간복잡도 ( Space Complexity ) : O( V ) ( V : 정점 개수 )
다익스트라 알고리즘의 경우, Prime`s MST ( Minest Spanning Tree ) 알고리즘과 유사하다.
루트를 기준으로, 두 집합을 유지한다.
한 집합은 최단경로트리에 포함된 정점을 포함하며,
다른 집합은 최단경로트리에 아직 포함되지 않은 정점을 포함한다.
알고리즘의 모든 단계에서 다른집합 ( 아직 포함되지 않은 집합 ) 에 있고 루트로부터 최소 거리를 가진 정점을 찾는다.
아래 예시를 살펴보자.
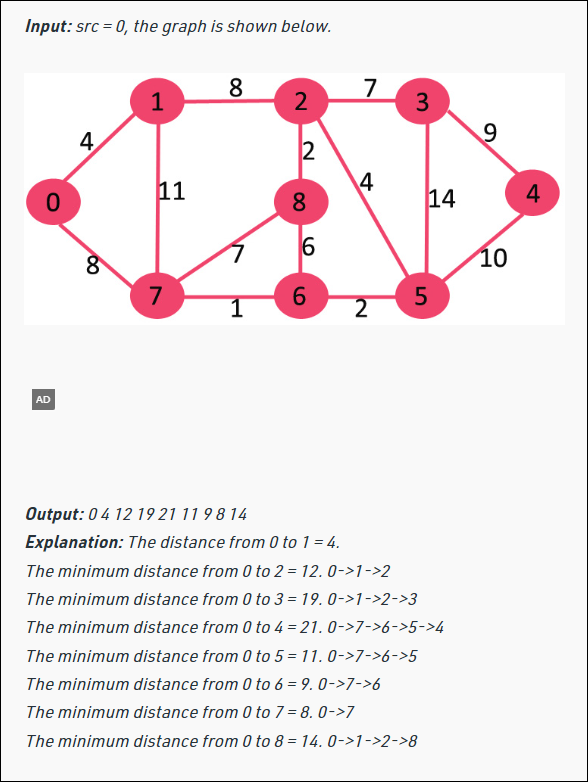
위 그래프를 예시로 들었을때, 출발지를 0번 정점이라고 잡았을때, 각 정점까지의 이동했을때 들어가는 최소비용(최단거리) 를 나타낸 그림이다.
어떤식으로 저렇게 각 정점까지의 최단거리를 구하는지 한 단계씩 알아보자.
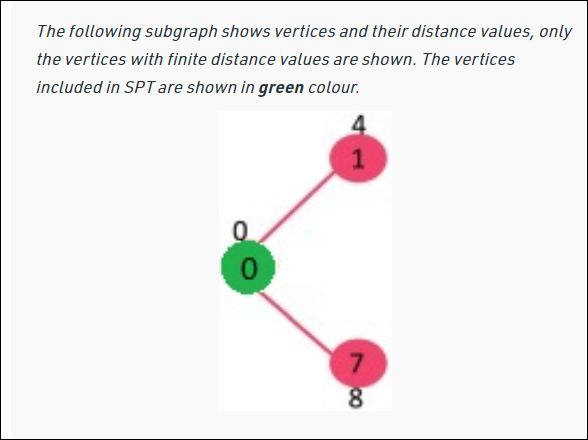
1. sptSet ( shortest path tree : 최단경로트리 ) 를 세팅시켜준다. => 각 정점까지의 최단거리가 계산되고 계속 정점을 추적해서 갱신하는 트리
2. 입력 그래프의 모든 정점에 거리 값을 할당한다. 처음에는 모든 거리값을 INFINITE 로 초기화한다. 처음 시작점으로 선택된 정점의 경우, 거리를 0으로 세팅한다.
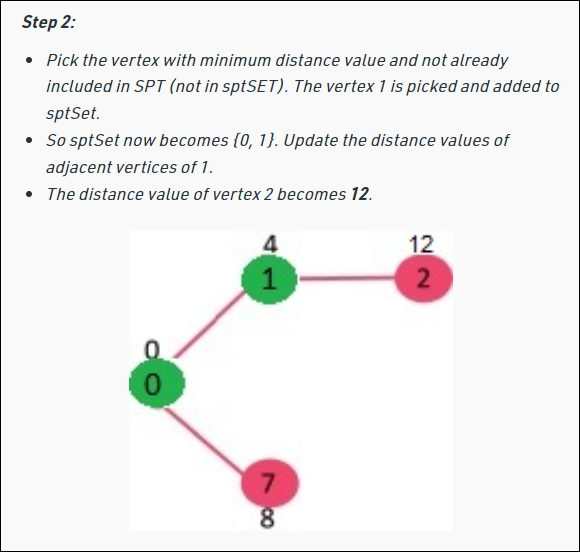
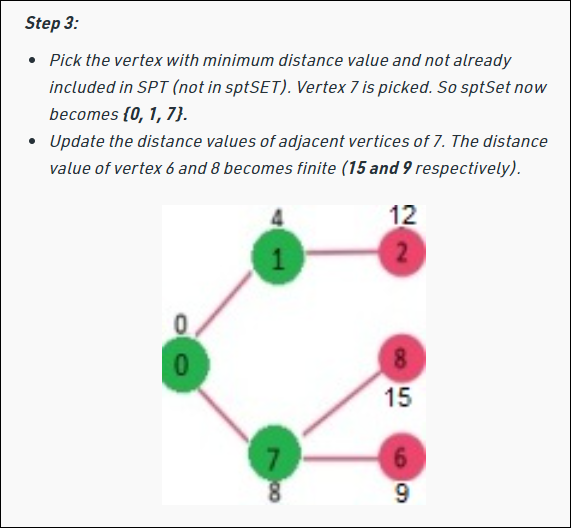
3. sptSet 은 최소거리 값을 가진 정점 u를 세팅한다. ( 따라서 모든 정점을 포함하지 않을 수 있음 )
4. 다음으로, 정점 u 의 모든 인접 정점의 거리값을 업데이트 한다.
거리값을 업데이트 하려면, 인접한 모든 정점도 살펴본다.
5. 인접한 정점을 v라고 할 때, u 정점에서 모든 인접한 v 까지의 거리의 합이 가장 작은경우가 있다면, 현재 v값을 갱신한다.
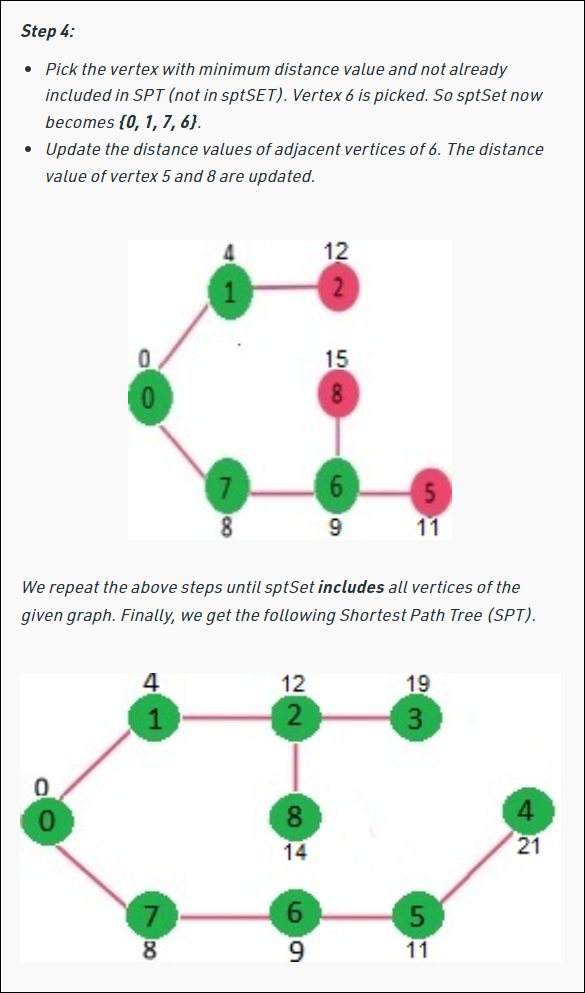
이런 방식을 위 그림에 적용해보자.
이제 코드로 구현해보자.
#include <iostream>#include <limits.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_V 9
// Find the vertex with minimum distance value,// from the set of vertices not yet included// in shortest path treeint minDistance(int dist[], bool sptSet[]){// Initialize min valueint min = INT_MAX;int min_index;
for (int v = 0; v < MAX_V; ++v){if (sptSet[v] == false && dist[v] <= min){min = dist[v];min_index = v;}}
return min_index;}
void printSolution(int dist[]){cout << "Vertex Distance from Source\n";for (int i = 0; i < MAX_V; ++i){cout << i << " " << dist[i] << '\n';}}
void dijkstra(int graph[MAX_V][MAX_V], int src){// output array. dist[i] will hold the// shortest distance from src to iint dist[MAX_V];
// sptSet[i] will be true if vertex i is included in// shortest path tree or shortest distance from src to i is finalizedbool sptSet[MAX_V];
// Initialize all distances as INFINITE and sptSet[] as falsefor (int i = 0; i < MAX_V; ++i){dist[i] = INT_MAX;sptSet[i] = false;}
// Distance of source vertex from itself is always 0dist[src] = 0;
for (int count = 0; count < MAX_V - 1; ++count){// Pick the minumum distance vertex from the set of// vertices not yet processed.// u is always equal to// src in the first iterationint u = minDistance(dist, sptSet);
// Mark the picked vertex as processedsptSet[u] = true;
// Update dist[v] only if is not in sptSet,// there is an edge from u to v, and total// weight of path from src to v through u is// smaller than current value of dist[v]for (int v = 0; v < MAX_V; ++v){if (!sptSet[v] && graph[u][v]&& dist[u] != INT_MAX&& dist[u] + graph[u][v] < dist[v]){dist[v] = dist[u] + graph[u][v];}}}
printSolution(dist);}
int main(){// Example graphint graph[MAX_V][MAX_V] ={{ 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0} ,{ 4, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0 },{ 0, 8, 0, 7, 0, 4, 0, 0, 2 },{ 0, 0, 7, 0, 9, 14, 0, 0, 0 },{ 0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0 },{ 0, 0, 4, 14, 10, 0, 2, 0, 0 },{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1, 6 },{ 8, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 7 },{ 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 0 }};
dijkstra(graph, 0);
return 0;}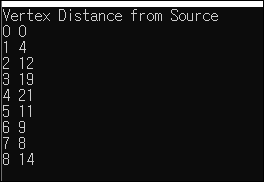
-----------------------------------
단, 다익스트라 알고리즘의 경우, 음수간선이 있는 그래프에서는 사용할 수 없기에 그래프가 어떤식으로 구축됬는지에 따라 쓸 수 있을수도 있고 없을수도 있다.
'자료구조 & 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
KMP 알고리즘 (0) 2023.01.09 Naive Pattern Searching 알고리즘 ( 무식하게 패턴찾기 ) (1) 2023.01.08 Pattern Searching 알고리즘 (0) 2023.01.07